From zero to a blank world map
When you need to show a web map you normally end up using something like:
var map = L.map('map').setView([38.736946, -9.142685], 3);
L.tileLayer('http://{s}.tile.osm.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png').addTo(map);But what does it take to show that map? What software stack lays behind the curtains? And how can you customize the map? Lets find out!
We start from a vanilla Linux Virtual Machine and end up showing a humble web map – a blank world – the hello world of maps.
Be warned that I barely describe the terms used in the GIS world. Be sure to read the referenced material for more information.
So, lets get cooking!
Ingredients
Recipe
Install Xubuntu
Install Xubuntu 14.10 (Utopic Unicorn) from torrent on a VirtualBox VM.
Make sure you give it some respectful resources. I gave mine:
- 60GB of disk
- 4GB of memory
- 2 CPUs
- 64MB of video memory
After install, bring it up to date. Open a Terminal Emulator and type:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-get clean
sudo rebootInstall the VirtualBox Guest Additions. On the VM VirtualBox UI select Devices, Insert Guest Additions CD Image.... Xubuntu should automatically mount the CD. Open a terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install dkms
cd /media/$USER/VBOX*
sudo ./VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
sudo rebootIn order to copy the commands from this article into the VM you should enable the shared clipboard. On the VM VirtualBox UI select the Devices, Shared Clipboard, Bidirectional.
Mapbox Studio
Studio is used to quickly style maps.
Install it with:
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:chris-lea/node.js
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install nodejs
sudo apt-get install git
git clone https://github.com/mapbox/mapbox-studio.git
cd mapbox-studio
npm installNB I’ve got revision 953ecc.
Start Studio:
npm startOn the Terminal, Right-Click the http://localhost:3000 text and select Open Link. Or open the Firefox Web Browser
from the Xfce menu. Or in a second Terminal type:
exo-open http://localhost:3000Follow the application steps to create a free Mapbox account. After that, you are ready to use Studio.
Coastline data
The Coastline is the line where the land meets the sea. We’ll use it to draw the world outline on our map.
The Coastline data is maintained by the OpenStreetMap contributors. Its periodically extracted from OpenStreetMap and made available at the OpenStreetMap Data site as a Shapefile – created by the OSMCoastline application.
This data is available in two different projections (aka SRS):
- EPSG:4326 (aka WGS84). Used in GPS and raw OpenStreetMap data found on Planet.osm.
- EPSG:3857 (aka Web Mercator or Spherical Mercator aka 900913). Used in web maps (e.g. Google/Bing/Leaftlet/Mapbox.js).
NB You should prefer EPSG:3857 because its the one normally used in web maps – no re-projection will be needed.
NB Be sure to known your coordinates projection – otherwise confusion will surely arise!
Download the Coastline water polygons Shapefile (~390MB) – EPSG:3857 projection:
sudo apt-get install curl
curl -O http://data.openstreetmapdata.com/water-polygons-split-3857.zip
unzip water-polygons-split-3857.zipAnd index it:
~/mapbox-studio/node_modules/mapnik/lib/binding/node-v11-linux-*/shapeindex water-polygons-split-3857/water_polygons.shpSource
To show any data in Studio we need to have a Source.
NB A Studio Source handles both of the projections mentioned before. But if you use EPSG:3857 no re-projection will be needed.
To create one, go to Studio, and:
- Click the
Projectsicon (bottom-left corner). - Click the
New Projecticon. - Click the
Blank sourceicon (right column).
Create a new layer for the data:
- Click the
New Layericon (top-right). - Click the
Browsebutton and select thewater-polygons-split-3857/water_polygons.shpfile. - Click the
renamelink and rename the layer tocoastalarea. You will later use it in a stylesheet selector as#coastalarea. - Click the
Donebutton.
Change the project settings:
- Click the
Settingsbutton (left toolbar). - Change the Maxzoom value to
22. - Click the
Save asbutton (left toolbar). - Save the Source project as
blank-world.
You should now have on your disk a blank-world.tm2source directory. It contains all the Source project files.
You are now ready to create a Style project.
Style
Maps are styled with CartoCSS – a language similar to CSS.
Lets use it to style the map.
Go to Studio and create a new Style project:
- Click the
Projectsicon (bottom-left corner). - Click the
New Projecticon. - Click the
Basicstyle icon (left column).
You should now see a basic map; but we want to use our own Source, so:
- Click the
Layersicon. - Click the
Change sourceicon. - Toggle the Sources to
Local. - Select the
blank-world.tm2sourceSource that we’ve created before. - Click the
Save asbutton (left toolbar). And save the project asblank-world.
On your disk, you should now have a blank-world.tm2 directory. It contains all the Style project files.
You should also notice a Style pane on the right hand side of the window. It contains the stylesheet that is used to style the map. Replace the text with:
@land: #f8f4f0;
@water: #a0c8f0;
Map {
background-color: @land;
}
#coastalarea {
line-color: @water;
polygon-fill: @water;
}Save the Project (press Ctrl+S).
After a bit, you should see a map!
Tile server
To display a map on a web page we need:
- A server that returns the map as Tile images.
- A HTML widget that displays them.
We’ll use the tessera server. Install it with:
mkdir blank-world && cd blank-world
cat<<"EOF">package.json
{
"name": "blank-world",
"version": "1.0.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {}
}
EOF
npm install tessera --save
npm install tilelive-tmsource --save
npm install tilelive-tmstyle --saveSee the resulting dependencies and versions:
cat package.jsonI got:
"tessera": "^0.5.1",
"tilelive": "^5.4.1",
"tilelive-tmsource": "^0.1.2",
"tilelive-tmstyle": "^0.3.0",
"tilelive-vector": "^2.3.1"Start tessera:
./node_modules/.bin/tessera tmstyle://$HOME/blank-world.tm2It should now be running at http://localhost:8080.
In another Terminal, get the TileJSON document that describes the map:
sudo apt-get install httpie
http get http://localhost:8080/index.jsonYou should see something like:
{
"attribution": "...",
"bounds": [
-180,
-85.0511,
180,
85.0511
],
"center": [ ... ],
"format": "png8:m=h",
"maxzoom": 22,
"minzoom": 0,
"name": "Untitled",
"scale": "1",
"source": "tmsource:///home/rgl/blank-world.tm2source",
"tilejson": "2.0.0",
"tiles": [
"http://localhost:8080/{z}/{x}/{y}.png"
]
}You can also get a Tile image, e.g. the south of Portugal:
curl -O http://localhost:8080/6/30/24.png
exo-open 24.pngTiles are normally PNG images with 256x256 pixels.
You are almost done! Off to showing the web map…
Web map
To show the map we’ll use the Mapbox.js library.
Create the web page:
cat<<"EOF">map.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset='utf-8' />
<title>blank world</title>
<meta name='viewport' content='initial-scale=1,maximum-scale=1,user-scalable=no' />
<script src='https://api.tiles.mapbox.com/mapbox.js/v2.1.4/mapbox.js'></script>
<link href='https://api.tiles.mapbox.com/mapbox.js/v2.1.4/mapbox.css' rel='stylesheet' />
<style>
body { margin:0; padding:0; }
#map { position:absolute; top:0; bottom:0; width:100%; }
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id='map'></div>
<script>
var map = L.mapbox.map('map', 'http://localhost:8080/index.json')
.setView([38.736946, -9.142685], 3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
EOFOpen it:
exo-open map.htmlYou should now see the blank world map!
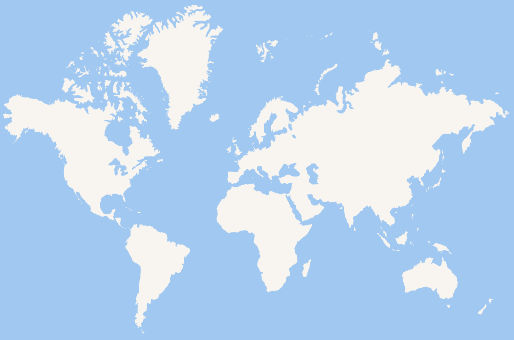
And there you have it! Let me known how it worked for you.
In a future article I’ll show you how to import the water areas from OpenStreetMap.
More information
This article mentioned a lot of pieces that you might not be familiar with. To get more insight you should read the following references:
Map Styles:
Map projections (aka SRS):
- EPSG:4326 (aka WGS84). Used in GPS and raw OpenStreetMap data found on Planet.osm.
- EPSG:3857 (aka Web Mercator or Spherical Mercator). Used in web maps (e.g. Google/Bing/Leaftlet/Mapbox.js).
- FAQ
- The Google Maps / Bing Maps Spherical Mercator Projection confusion.
As an alternative software stack, you should look at:
And finally, feel free to contact me!
– RGL